Difference between revisions of "Types of Data"
From IMSMA Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Raster vs Vector a.jpg|400px|center]] | |
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | '' Raster vs. Vector Data '' | ||
| + | </div> | ||
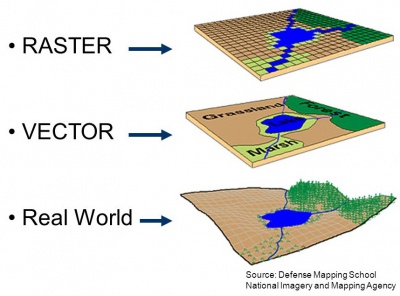
==Vector Data==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Vector Data==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Vector data comprises of vertices and paths. These include points (hospitals), lines (roads) and polygons (areas). | Vector data comprises of vertices and paths. These include points (hospitals), lines (roads) and polygons (areas). | ||
| Line 6: | Line 9: | ||
* Shape File (.shp) this is the standard file format for vector data and will contain only a single dataset | * Shape File (.shp) this is the standard file format for vector data and will contain only a single dataset | ||
* Geodatabase (.gdb) these will contain multiple datasets simultaneously. | * Geodatabase (.gdb) these will contain multiple datasets simultaneously. | ||
| + | [[Image:VECTOR Example.jpg|300px|left]] | ||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
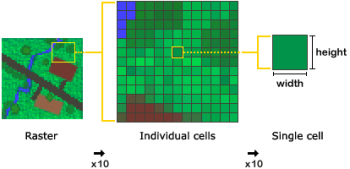
==Raster Data==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Raster Data==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Raster data is made up of pixels (also referred to as grid cells). Raster’s often look pixelated because each pixel is associated with a value or a class. Rasters include satellite and UAV/UAS imagery, elevation data models, etc. Common raster file formats are: | Raster data is made up of pixels (also referred to as grid cells). Raster’s often look pixelated because each pixel is associated with a value or a class. Rasters include satellite and UAV/UAS imagery, elevation data models, etc. Common raster file formats are: | ||
| − | * .jpeg, .png, .tiff, .bmp | + | * .jpeg, .png, .tiff, .bmp |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:RASTER Example.png|350px|left]] | ||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[http://gisgeography.com/spatial-data-types-vector-raster/ GIS Spatial Data Types: Vector vs Raster] | [http://gisgeography.com/spatial-data-types-vector-raster/ GIS Spatial Data Types: Vector vs Raster] | ||
{{NavBox Remote Sensing and Spatial Analysis}} | {{NavBox Remote Sensing and Spatial Analysis}} | ||
[[Category:PEW]] | [[Category:PEW]] | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 10 August 2016
Raster vs. Vector Data
Vector Data
Vector data comprises of vertices and paths. These include points (hospitals), lines (roads) and polygons (areas). Vector data can be in various data formats, these include:
- KML, KMZ (often used in Google Earth or other web GIS programs)
- Shape File (.shp) this is the standard file format for vector data and will contain only a single dataset
- Geodatabase (.gdb) these will contain multiple datasets simultaneously.
Raster Data
Raster data is made up of pixels (also referred to as grid cells). Raster’s often look pixelated because each pixel is associated with a value or a class. Rasters include satellite and UAV/UAS imagery, elevation data models, etc. Common raster file formats are:
- .jpeg, .png, .tiff, .bmp
GIS Spatial Data Types: Vector vs Raster
| |||||||||||