Difference between revisions of "Information Exchange"
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{TOC right}} | {{TOC right}} | ||
| − | {{IMSMANG}} is designed to support information exchange with many IMSMA users and Mine Action stakeholders at numerous sites. These users can include implementing partners, Regional Mine Action Centers and other authorities (e.g. Ministry of Health). | + | {{IMSMANG}} is designed to support data/information exchange with many IMSMA users and Mine Action stakeholders at numerous sites. These users can include implementing partners, Regional Mine Action Centers and other authorities (e.g. Ministry of Health). |
| − | {{IMSMANG}} supports | + | {{IMSMANG}} supports several patterns for exchanging '''data''' including |
| − | * | + | * one-direction exchange |
| + | * two-direction exchange | ||
* peer-to-peer exchange | * peer-to-peer exchange | ||
| − | * | + | * combinations of the above. |
| − | + | ||
| + | {{HowTo's | ||
| + | | [[Information Exchange Models]] | ||
| + | | Centralised Data Entry | ||
| + | | [[Setting-up Decentralised Information Exchange | Decentralised Data Entry]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
The most common pattern is two-direction exchange between a Central Mine Action Authority and implementing partners. | The most common pattern is two-direction exchange between a Central Mine Action Authority and implementing partners. | ||
| − | {{IMSMANG}} supports | + | {{IMSMANG}} supports several methods for exchanging '''information''' including |
| − | * producing maps with external GIS software | + | * producing maps with [[Connecting to IMSMA Staging area from ArcGIS | external GIS]] software |
| − | * producing reports with iReport and Excel | + | * producing reports with [[Use iReport | iReport]] and [[Connecting to IMSMA Staging area from Excel | Excel]] |
| − | + | * publish information to websites via the [[IMSMA Staging Area]]. | |
| − | * publish information to websites via the Staging | + | |
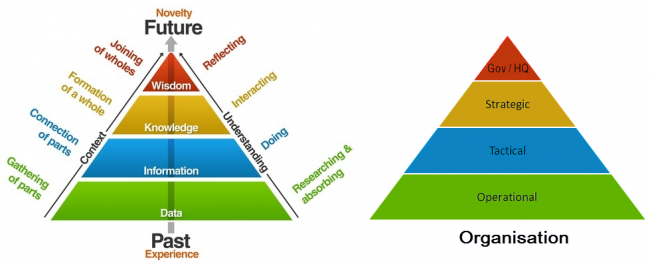
| + | [[Image:Data Information Organisation.png|650px|center]] | ||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | '' Who needs what'' | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | An important part of establishing data/information exchange is to plan and document the data/informations exchange flows including the different steps in the workflows so a sustainable and smooth exchanges and high-quality information are obtained. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Plan Data/Information Exchange==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
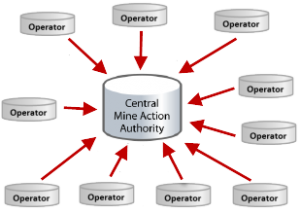
| + | | [[Image:Understanding Configuration Options - One way.png|300px|center|]] | ||
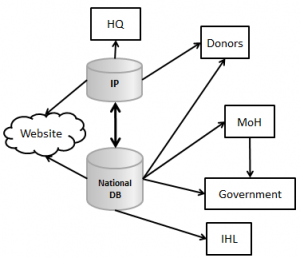
| + | | [[Image:Information exchange.png|300px|center|]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '' One way exchange plan only covering operators and national database '' | ||
| + | | '' Example of information exchange between stakeholders'' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is easy for information managers at national level only to concentrate on how to exchange data that should be imported into the national {{IMSMANG}} database and forget that it should be a '''two'''-directional exchange and that '''all''' implementation partners, stakeholders and departments of the own organisation have different data/information needs and '''all''' of them have to create reports to several other receivers with different contents and with different periodicity. | ||
| − | + | The following points need to be taken in consideration when planning exchange: | |
| + | * why is the data/information shared? | ||
| + | * what are the consequences if data/information are not shared on time? | ||
| + | * what data/information need/could be shared? | ||
| + | * who is the receiver? | ||
| + | * what will the receiver use the data/information for? | ||
| + | :* show contamination impact | ||
| + | :* input to operational planning | ||
| + | :* show the outcome of Mine Action | ||
| + | :* other purposes | ||
| + | * will the receiver share the data/information in his turn? | ||
| + | * how often? | ||
| + | * in which format? | ||
| + | :* paper/pdf | ||
| + | :* Excel | ||
| + | :* shape files | ||
| + | :* xml | ||
| + | :* IMSMA backup | ||
| + | :* Staging area database | ||
| + | :* website | ||
| − | == | + | ==Workflows==__NOEDITSECTION__ |
| − | + | When the plan for data/information exchange is outlined it is very important to document the different exchanges so it is clear to all stakeholders in each data/information exchange workflow: | |
| + | * who does what? | ||
| + | * how often? | ||
| + | * who is responsible for data quality? | ||
| + | * who solves data conflicts including duplicates? | ||
| + | * how and who corrects mistakes? | ||
| + | * who deletes data? | ||
| + | |||
| + | A process map of each exchange workflow is a good complement to the detailed written documentation of the workflow. | ||
| − | + | ==IMSMA specific rules==__NOEDITSECTION__ | |
| − | + | Data exchange workflows to the national database should include: | |
| − | * | + | * how to decide which Location to use? |
| − | * | + | * which items should have links to what? |
| − | * | + | * nice-to-have - desired - required data fields |
| − | * | + | * who decides final ID of items? |
| − | + | {{Note | When data is shared between implementing partners and National Mine Action Authority it is important that IDs are '''not''' changed. E.g. Progress report created by implementing partner with ID ''PR-NPA-CHA-15/1'' should still have the same ID after import and approval in the national database.}} | |
| − | ==Ensuring Correct Roles and Permissions are Assigned==__NOEDITSECTION__ | + | ===Ensuring Correct Roles and Permissions are Assigned===__NOEDITSECTION__ |
| − | Establishing correct roles and permissions is a key factor in managing and maintaining data exchange | + | Establishing correct [[Defining Roles, Permissions and Users | roles and permissions]] in {{IMSMANG}} is a key factor in managing and maintaining data exchange with {{IMSMANG}}. Using the permissions structure, the information manager can carefully control access to key functions that affect data exchange including Data Entry Form templates, Custom Defined Fields, Auxiliary data and Data Entry Form approval. When permissions are correctly established and user accounts created, information managers can distribute the {{IMSMANG}} dataset to implementing partners knowing that key data controls are in place. |
These are the recommended role permissions: | These are the recommended role permissions: | ||
| − | * Ensure that the Central Mine Action Authority has exclusive control over user accounts and roles | + | * Ensure that the Central Mine Action Authority has exclusive control over |
| + | :* user accounts and roles | ||
| + | :* Data Entry Form templates | ||
| + | :* Data Inventory Manager and | ||
| + | :* Auxiliary data. | ||
* Ensure that the implementing partners have Data Entry, Approval and export/import Data Entry Forms permissions. | * Ensure that the implementing partners have Data Entry, Approval and export/import Data Entry Forms permissions. | ||
| − | + | By establishing a set of limited permissions for the implementing partners, information managers can prevent the accidental or intentional creation of new data elements that will affect the ability of the Central Mine Action Authority to import Data Entry Forms and cause the national dataset to become fractured. | |
| − | By establishing a set of limited permissions for the implementing partners, information managers can prevent the accidental or intentional creation of new data elements | ||
| − | By limiting Auxiliary data permissions to the Central Mine Action Authority, information managers can prevent complications when importing Data Entry Forms. Because Data Entry Forms refers to Auxiliary data, it is important that each country have one common set of Auxiliary data to facilitate exchange. If the Auxiliary data is not properly synchronised, the exchange of Data Entry Forms can result in import issues which must be manually resolved. While {{IMSMANG}} provides an interface for resolving these kinds of issues, it is recommended to reduce the occurrence of these issues by limiting any creation of Auxiliary data to the Central Mine Action Authority who can then distribute an updated dataset as necessary. | + | By limiting Auxiliary data permissions to the Central Mine Action Authority, information managers can prevent complications when importing Data Entry Forms. Because Data Entry Forms refers to Auxiliary data, it is important that each country have one common set of [[Standardising Auxiliary Data | Auxiliary data]] to facilitate exchange. If the Auxiliary data is not properly synchronised, the exchange of Data Entry Forms can result in import issues which must be manually resolved. While {{IMSMANG}} provides an interface for resolving these kinds of issues, it is recommended to reduce the occurrence of these issues by limiting any creation of Auxiliary data to the Central Mine Action Authority who can then distribute an updated dataset as necessary. |
| − | == | + | ==Collecting Regular Feedback==__NOEDITSECTION__ |
| − | + | In any data/information exchange activity, it is important to have regular follow-up or meetings to collect feedback and discuss issues or improvements to the data/information exchange process. One recommendation is to establish a feedback forum where implementing partners and stakeholders can address data quality issues and make adjustments to the data/information exchange process. Topics to address in such a forum include: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * frequency of data/information exchange | ||
| + | * standardisation of reports and searches to be included in the central dataset | ||
| + | * permissions and role changes | ||
| + | * creation or modification of Auxiliary data | ||
| + | * which data to collect | ||
| + | * changes of templates | ||
| + | * output products like reports, statistics, maps | ||
| + | By collecting feedback on these points, information managers can help ensure that data/information exchange works as expected and set up a quality assurance mechanism to prevent data quality issues from affecting the Mine Action Programme. | ||
| − | {{NavBox | + | {{NavBox IMSMA NG Administration}} |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:NAA]] |
Latest revision as of 12:08, 4 May 2021
IMSMANG is designed to support data/information exchange with many IMSMA users and Mine Action stakeholders at numerous sites. These users can include implementing partners, Regional Mine Action Centers and other authorities (e.g. Ministry of Health).
IMSMANG supports several patterns for exchanging data including
- one-direction exchange
- two-direction exchange
- peer-to-peer exchange
- combinations of the above.
| How To |
|---|
|
The most common pattern is two-direction exchange between a Central Mine Action Authority and implementing partners.
IMSMANG supports several methods for exchanging information including
- producing maps with external GIS software
- producing reports with iReport and Excel
- publish information to websites via the IMSMA Staging Area.
Who needs what
An important part of establishing data/information exchange is to plan and document the data/informations exchange flows including the different steps in the workflows so a sustainable and smooth exchanges and high-quality information are obtained.
Contents
Plan Data/Information Exchange
| One way exchange plan only covering operators and national database | Example of information exchange between stakeholders |
It is easy for information managers at national level only to concentrate on how to exchange data that should be imported into the national IMSMANG database and forget that it should be a two-directional exchange and that all implementation partners, stakeholders and departments of the own organisation have different data/information needs and all of them have to create reports to several other receivers with different contents and with different periodicity.
The following points need to be taken in consideration when planning exchange:
- why is the data/information shared?
- what are the consequences if data/information are not shared on time?
- what data/information need/could be shared?
- who is the receiver?
- what will the receiver use the data/information for?
- show contamination impact
- input to operational planning
- show the outcome of Mine Action
- other purposes
- will the receiver share the data/information in his turn?
- how often?
- in which format?
- paper/pdf
- Excel
- shape files
- xml
- IMSMA backup
- Staging area database
- website
Workflows
When the plan for data/information exchange is outlined it is very important to document the different exchanges so it is clear to all stakeholders in each data/information exchange workflow:
- who does what?
- how often?
- who is responsible for data quality?
- who solves data conflicts including duplicates?
- how and who corrects mistakes?
- who deletes data?
A process map of each exchange workflow is a good complement to the detailed written documentation of the workflow.
IMSMA specific rules
Data exchange workflows to the national database should include:
- how to decide which Location to use?
- which items should have links to what?
- nice-to-have - desired - required data fields
- who decides final ID of items?
Ensuring Correct Roles and Permissions are Assigned
Establishing correct roles and permissions in IMSMANG is a key factor in managing and maintaining data exchange with IMSMANG. Using the permissions structure, the information manager can carefully control access to key functions that affect data exchange including Data Entry Form templates, Custom Defined Fields, Auxiliary data and Data Entry Form approval. When permissions are correctly established and user accounts created, information managers can distribute the IMSMANG dataset to implementing partners knowing that key data controls are in place.
These are the recommended role permissions:
- Ensure that the Central Mine Action Authority has exclusive control over
- user accounts and roles
- Data Entry Form templates
- Data Inventory Manager and
- Auxiliary data.
- Ensure that the implementing partners have Data Entry, Approval and export/import Data Entry Forms permissions.
By establishing a set of limited permissions for the implementing partners, information managers can prevent the accidental or intentional creation of new data elements that will affect the ability of the Central Mine Action Authority to import Data Entry Forms and cause the national dataset to become fractured.
By limiting Auxiliary data permissions to the Central Mine Action Authority, information managers can prevent complications when importing Data Entry Forms. Because Data Entry Forms refers to Auxiliary data, it is important that each country have one common set of Auxiliary data to facilitate exchange. If the Auxiliary data is not properly synchronised, the exchange of Data Entry Forms can result in import issues which must be manually resolved. While IMSMANG provides an interface for resolving these kinds of issues, it is recommended to reduce the occurrence of these issues by limiting any creation of Auxiliary data to the Central Mine Action Authority who can then distribute an updated dataset as necessary.
Collecting Regular Feedback
In any data/information exchange activity, it is important to have regular follow-up or meetings to collect feedback and discuss issues or improvements to the data/information exchange process. One recommendation is to establish a feedback forum where implementing partners and stakeholders can address data quality issues and make adjustments to the data/information exchange process. Topics to address in such a forum include:
- frequency of data/information exchange
- standardisation of reports and searches to be included in the central dataset
- permissions and role changes
- creation or modification of Auxiliary data
- which data to collect
- changes of templates
- output products like reports, statistics, maps
By collecting feedback on these points, information managers can help ensure that data/information exchange works as expected and set up a quality assurance mechanism to prevent data quality issues from affecting the Mine Action Programme.
| |||||||||||||||||||