Difference between revisions of "Standardising Data Analysis and Information Reporting"
m |
|||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC right}} | {{TOC right}} | ||
| − | + | Two of most important purposes of an information system are: | |
| − | + | * ensure high quality of data and | |
| + | * support operational use of the information. | ||
| + | One important use of the data is reporting. If it not possible in an easy way to create reports/statistics which reflect the data correctly the credibility of the data is lost. That’s why {{IMSMANG}} was designed with a robust reporting and analysis component that supports various reporting options. These options include: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| − | {| class="wikitable" width=" | + | {| class="wikitable" width="1000" |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center" colspan=" | + | | align="center" colspan="6" | '''Comparison of {{IMSMANG}} Reporting Options''' |
|- | |- | ||
| width="20pt" | | | width="20pt" | | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
| width="195pt" | '''iReport''' | | width="195pt" | '''iReport''' | ||
| width="195pt" | '''Data export''' | | width="195pt" | '''Data export''' | ||
| − | | width="195pt" | ''' | + | | width="195pt" | '''Other external reporting tool''' |
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" | '''Description''' | | align="left" | '''Description''' | ||
| − | | align="left" | Includes printing | + | | align="left" | Includes printing Data Entry Forms, Summary items and maps |
| align="left" | Includes building iReport templates for more sophisticated reporting as well as exporting data for use in external tools such as Microsoft Excel | | align="left" | Includes building iReport templates for more sophisticated reporting as well as exporting data for use in external tools such as Microsoft Excel | ||
| align="left" | Includes exporting data to CSV format for use in Excel as well as cutting and pasting from tables. | | align="left" | Includes exporting data to CSV format for use in Excel as well as cutting and pasting from tables. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 23: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="left" | '''Uses''' | | align="left" | '''Uses''' | ||
| − | | align="left" | Navigating data in | + | | align="left" | |
| − | General summaries of pre-provided data | + | *Navigating data in {{IMSMANG}} |
| + | *General summaries of pre-provided data | ||
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
*Lists and summary reports of single items | *Lists and summary reports of single items | ||
*Simple cross tabs | *Simple cross tabs | ||
*Monthly progress reports for internal consumption | *Monthly progress reports for internal consumption | ||
| − | * | + | *Charts |
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
*Manipulating data using external tools | *Manipulating data using external tools | ||
*Pivot tables and charts based on one item | *Pivot tables and charts based on one item | ||
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
| − | *Linking or exporting | + | *Linking or exporting {{IMSMANG}} data for use in external tools |
| − | *Building customised reporting tools for | + | *Building customised reporting tools for {{IMSMANG}} data |
*Linking data to ArcGIS Desktop, Crystal Reports and other tools | *Linking data to ArcGIS Desktop, Crystal Reports and other tools | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 47: | Line 50: | ||
*Supports charts | *Supports charts | ||
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
| − | *Easiest way to get | + | *Easiest way to get {{IMSMANG}} data into Excel |
*Can manipulate data in common applications | *Can manipulate data in common applications | ||
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
| Line 59: | Line 62: | ||
*Limited to printing and reports provided with the software. No customisation. | *Limited to printing and reports provided with the software. No customisation. | ||
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
| − | |||
*Not ideal for incorporating multiple reports together within a larger report | *Not ideal for incorporating multiple reports together within a larger report | ||
| align="left" | | | align="left" | | ||
| Line 68: | Line 70: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | [[Image:BI in context graph.png|center|700px']] | ||
| + | |||
==Basic Reporting==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Basic Reporting==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | + | {{IMSMANG}} provides several reporting options that allow users to produce basic reports directly from {{IMSMANG}}. These include printing Data Entry Forms entered into the system, maps from the main navigation window and Summary items. Any of these reports can be sent directly to a printer or to an intermediate format such as rich text format (.RTF) or portable document format (.PDF) for transmitting in electronic format or for further editing. | |
| − | + | {{IMSMANG}} also includes a Map Layout manager that allows users to define map layouts and print high-quality maps with {{IMSMANG}} data. Information managers can define map layout templates that include scale bars, annotations and legends or use more sophisticated tools like ArcGIS Desktop to prepare more complicated map layouts for displaying {{IMSMANG}} data. | |
[[Image:AdminGuide_ExampleMapLayoutTemplate.png|center|500px|''Example of a Map Layout Template'']] | [[Image:AdminGuide_ExampleMapLayoutTemplate.png|center|500px|''Example of a Map Layout Template'']] | ||
| Line 80: | Line 84: | ||
{{note| | {{note| | ||
| − | * Map layouts can be printed and scaled to any size paper. This is a simple way of producing | + | * Map layouts can be printed and scaled to any size paper. This is a simple way of producing {{IMSMANG}} maps without needing additional GIS software. |
| − | * Map layout templates can be prepared and distributed to individual | + | * Map layout templates can be prepared and distributed to individual {{IMSMANG}} clients, allowing information managers to prepare templates based on user preferences or functional needs. |
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Embedded Reporting==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Embedded Reporting==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | + | {{IMSMANG}} supplements the basic reporting options available to all users with several more sophisticated reporting tools that are embedded within the system. In addition to reporting on individual elements, these embedded tools allow for statistical and aggregate reporting of data within the database. Instead of reporting the contents of a single report, statistical reporting allows information managers to produce reports about multiple items and to use functions such as sum, average and count to summarise data. | |
| − | There are two options for embedded reporting: iReports and data export. Both functions rely on | + | There are two options for embedded reporting: iReports and data export. Both functions rely on {{IMSMANG}} searches to filter data. Using iReports, information managers can build reporting templates to visualise data in a specific and repeatable format. Using data export, managers can export search results to an external tool such as Microsoft Excel and perform aggregation and statistical analysis. |
===iReports===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ===iReports===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | With the iReport tool, information managers have access to an entire suite of report generation functions. iReport provides the ability to design report templates from the desired data elements; add page layout and formatting information including images, colours and text; and import the reports into | + | {{HowTo's |
| + | |[[Use iReport | Use iReport]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | With the iReport tool, information managers have access to an entire suite of report generation functions. iReport provides the ability to design report templates from the desired data elements; add page layout and formatting information including images, colours and text; and import the reports into {{IMSMANG}} for data entry personnel to run. Information managers can also design complex reports to summarise data using sum, count, average, subreports and other statistical reporting functions similar to packages such as Crystal Reports. Being fully integrated into {{IMSMANG}}, iReport can be translated into any language supported by the system. Using this approach, only information managers are presented with the complexity of designing reports while traditional users simply have to select a report (and any preceding search) and run it. | ||
Typical uses for iReport include producing reports commonly required by multiple users within a programme. These reports can include: | Typical uses for iReport include producing reports commonly required by multiple users within a programme. These reports can include: | ||
| Line 105: | Line 107: | ||
*data quality: number and list of land with incorrect status | *data quality: number and list of land with incorrect status | ||
| − | Because iReport templates are initiated with a search, they provide a scalable reporting solution that allows one template to be developed for many reports. For example, a report template that shows | + | Because iReport templates are initiated with a search, they provide a scalable reporting solution that allows one template to be developed for many reports. For example, a report template that shows a list of land with associated ordnance details can produce different reports depending on the search parameters. |
[[Image:AdminGuide_ReportUsingNoSearchParameters.png|center|500px|''Report Example Using No Search Parameters'']] | [[Image:AdminGuide_ReportUsingNoSearchParameters.png|center|500px|''Report Example Using No Search Parameters'']] | ||
| Line 112: | Line 114: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | In the first example, no search parameter is applied and all data in | + | In the first example, no search parameter is applied and all data in {{IMSMANG}} is used in the report. But by adding a search parameter, for example, limiting this to land whose status is Worked on, a different report is generated. |
[[Image:AdminGuide_ReportUsingSearchParameters.png|center|500px|''Report Example Using a Search Parameter'']] | [[Image:AdminGuide_ReportUsingSearchParameters.png|center|500px|''Report Example Using a Search Parameter'']] | ||
| Line 119: | Line 121: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | Moreover, if the land | + | Moreover, if the land is further limited to a specific type, another report is generated, using again the same template. This way, information managers can build templates and searches to fulfill multiple reporting needs. |
| − | Reports created with iReport can be printed directly within | + | Reports created with iReport can be printed directly within {{IMSMANG}} or saved to an intermediate format such as .RTF, .PDF or .XLS for electronic transmission or additional editing or inclusion in other reports. iReport supports the inclusion of charts, images and headers and footers, and it acts as a complete reporting package. |
| + | ===Data Export===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
{{HowTo's | {{HowTo's | ||
| − | |[[ | + | |[[Exporting| Export data]] |
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | {{IMSMANG}} also provides data export functionality designed to allow users to export data to external tools such as Microsoft Excel for additional reporting and analysis. This lets users take advantage of functionality in these tools such as sums, counts, charts, pivot tables and other data manipulation functions to format and present data. Users access this functionality by performing a search in {{IMSMANG}} and then exporting the results to .CSV format. Users can choose which columns to export, and the data can be manipulated in any external tool that supports .CSV. | |
| − | |||
| − | Because data export is initiated with a search, it provides a flexible approach for getting data to an external tool. However, once the data is used in a tool outside of | + | Because data export is initiated with a search, it provides a flexible approach for getting data to an external tool. However, once the data is used in a tool outside of {{IMSMANG}}, it is impossible to control how this data is manipulated which may limit the consistency of reports produced in this way. |
| − | {{note| | + | {{note|{{IMSMANG}} searches return information on only one item at a time, and data export is limited to the data returned by the search. Data from linked items (such as victim data linked to accidents) is not available for export.}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | }} | ||
==External Reporting Tools==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==External Reporting Tools==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | + | {{IMSMANG}} also allows information managers to connect advanced reporting tools such as Crystal Reports or ArcGIS Desktop directly to its relational database for highly advanced report generation. With this capability, information managers can use custom reporting solutions to connect with {{IMSMANG}}, allowing for complete control of {{IMSMANG}} outputs. Or, managers can modify existing reporting solutions to connect to {{IMSMANG}}, which leverages technology already implemented in the programme and limits the need for retraining. | |
| − | {{note| | + | {{note|When using external reporting tools we recommend to connect to the '''[[IMSMA Staging Area | Staging area]]''' instead of the {{IMSMANG}} database. It does require knowledge about the IMSMA data model. Contact contact your [[Information Management Team | GICHD IM advisor]] if you have questions.}} |
| − | ===Connecting External Reporting Tools===__NOEDITSECTION__ | + | ===Connecting other External Reporting Tools===__NOEDITSECTION__ |
| − | The process for connecting external reporting tools is essentially the same for all tools. External tools connect to the | + | The process for connecting external reporting tools is essentially the same for all tools. External tools connect to the {{IMSMANG}} relational database via an ODBC connection. Information managers establish this connection by installing the ODBC driver for PGSQL. When this is complete, information managers can connect any ODBC-compliant tool to the {{IMSMANG}} database, including reporting tools, other database packages and SQL management tools. Examples include: |
| − | Reporting tools | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | + | ! scope="col" | Reporting tools || scope="col" | Database packages || scope="col" | SQL management tools | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Crystal Reports || Microsoft Access || PGSQL Query Browser | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | ArcGIS Desktop || OpenOffice Base || Navicat | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | iReport || Microsoft SQL Server || TOAD SQL | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Microsoft Excel || Oracle || Heidi SQL | |
| − | SQL | + | |} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | When connecting an external reporting tool to | + | When connecting an external reporting tool to {{IMSMANG}}, it is recommended that information managers build database views within the database to do any necessary data transformations. While it is possible to directly import or connect {{IMSMANG}} database tables in external tools and perform transformations within the external tools, the recommended method is to do transformations within the {{IMSMANG}} database using database views and then import the resulting views into the external tools. |
| − | {{note|Building database views to transform data before importing it into other tools significantly reduces the performance hit associated with connecting external tools}} | + | {{note|Building database views to transform data before importing it into other tools significantly reduces the performance hit associated with connecting external tools.}} |
===Building Database Views===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ===Building Database Views===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | Building database views is the primary way of transforming data to support external reporting. Information managers can use SQL editing tools to build and save database queries as views that can be used to format data for easier reporting. Using database views, information managers can join data together into flat tables that allow for easier incorporation into reports or other analysis tools. Database views act like database tables and can be imported or queried from external tools. Moreover, views automatically refresh as data is added to | + | Building database views is the primary way of transforming data to support external reporting. Information managers can use SQL editing tools to build and save database queries as views that can be used to format data for easier reporting. Using database views, information managers can join data together into flat tables that allow for easier incorporation into reports or other analysis tools. Database views act like database tables and can be imported or queried from external tools. Moreover, views automatically refresh as data is added to {{IMSMANG}} and provide an up-to-date data source for other applications. |
| − | Using database views, information managers can perform statistical and other operations on the | + | Using database views, information managers can perform statistical and other operations on the {{IMSMANG}} set for reporting purposes including sum, count and average or more complicated functions available in SQL. These operations can be combined with search criteria to provide a highly precise mechanism for providing data to reports. For example, information managers can create a view that returns the name of each clearance and a sum of the hours worked, AP mines found and area cleared on all progress reports linked to each clearance. |
| − | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
{| class="wikitable" width="600" | {| class="wikitable" width="600" | ||
| Line 200: | Line 193: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | This view could then be pasted into Excel, linked with additional | + | This view could then be pasted into Excel, linked with additional {{IMSMANG}} data or external data or linked with a map to provide additional analysis. As such, database views provide a powerful way of formatting and analysing {{IMSMANG}} data. |
{{note| | {{note| | ||
| − | * Database views created in | + | * Database views created in {{IMSMANG}} are backed up by the {{IMSMANG}} backup functionality. However, it is important to correctly set the database permissions on views or it will cause problems when restoring the databases. |
| − | * Information managers should maintain separate files containing the view creation scripts so that they can be quickly and easily restored or modified. Using the CREATE OR | + | * Information managers should maintain separate files containing the view creation scripts so that they can be quickly and easily restored or modified. Using the CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW syntax from SQL is an easy way to build scripts for creating or replacing views if they already exist. |
}} | }} | ||
| − | {{NavBox | + | {{NavBox IMSMA NG Administration}} |
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:NAA]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:44, 4 May 2021
Two of most important purposes of an information system are:
- ensure high quality of data and
- support operational use of the information.
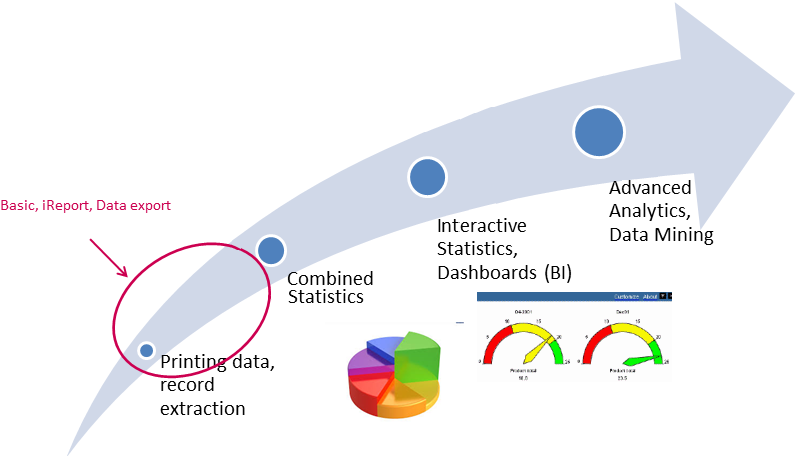
One important use of the data is reporting. If it not possible in an easy way to create reports/statistics which reflect the data correctly the credibility of the data is lost. That’s why IMSMANG was designed with a robust reporting and analysis component that supports various reporting options. These options include:
| Comparison of IMSMANG Reporting Options | |||||
| Basic | iReport | Data export | Other external reporting tool | ||
| Description | Includes printing Data Entry Forms, Summary items and maps | Includes building iReport templates for more sophisticated reporting as well as exporting data for use in external tools such as Microsoft Excel | Includes exporting data to CSV format for use in Excel as well as cutting and pasting from tables. | The most complicated kind of reporting where users connect to backend databases using SQL, Crystal Reports, ArcGIS Desktop, etc., to perform queries and generate reports | |
| Uses |
|
|
|
| |
| Benefits |
|
|
|
| |
| Challenges |
|
|
|
| |
Basic Reporting
IMSMANG provides several reporting options that allow users to produce basic reports directly from IMSMANG. These include printing Data Entry Forms entered into the system, maps from the main navigation window and Summary items. Any of these reports can be sent directly to a printer or to an intermediate format such as rich text format (.RTF) or portable document format (.PDF) for transmitting in electronic format or for further editing.
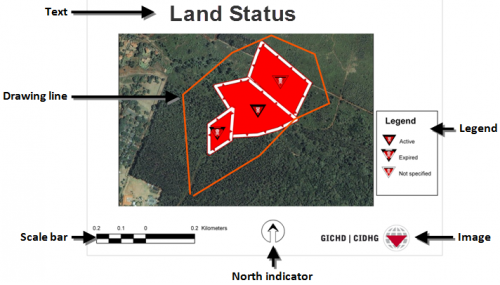
IMSMANG also includes a Map Layout manager that allows users to define map layouts and print high-quality maps with IMSMANG data. Information managers can define map layout templates that include scale bars, annotations and legends or use more sophisticated tools like ArcGIS Desktop to prepare more complicated map layouts for displaying IMSMANG data.
Example of a Map Layout Template
Embedded Reporting
IMSMANG supplements the basic reporting options available to all users with several more sophisticated reporting tools that are embedded within the system. In addition to reporting on individual elements, these embedded tools allow for statistical and aggregate reporting of data within the database. Instead of reporting the contents of a single report, statistical reporting allows information managers to produce reports about multiple items and to use functions such as sum, average and count to summarise data.
There are two options for embedded reporting: iReports and data export. Both functions rely on IMSMANG searches to filter data. Using iReports, information managers can build reporting templates to visualise data in a specific and repeatable format. Using data export, managers can export search results to an external tool such as Microsoft Excel and perform aggregation and statistical analysis.
iReports
| How To |
|---|
With the iReport tool, information managers have access to an entire suite of report generation functions. iReport provides the ability to design report templates from the desired data elements; add page layout and formatting information including images, colours and text; and import the reports into IMSMANG for data entry personnel to run. Information managers can also design complex reports to summarise data using sum, count, average, subreports and other statistical reporting functions similar to packages such as Crystal Reports. Being fully integrated into IMSMANG, iReport can be translated into any language supported by the system. Using this approach, only information managers are presented with the complexity of designing reports while traditional users simply have to select a report (and any preceding search) and run it.
Typical uses for iReport include producing reports commonly required by multiple users within a programme. These reports can include:
- clearance: monthly progress reporting
- education: number of people trained by type of training
- land: sum of hazardous area by province or type of land
- accidents: number of accidents by type or by province
- data quality: number and list of land with incorrect status
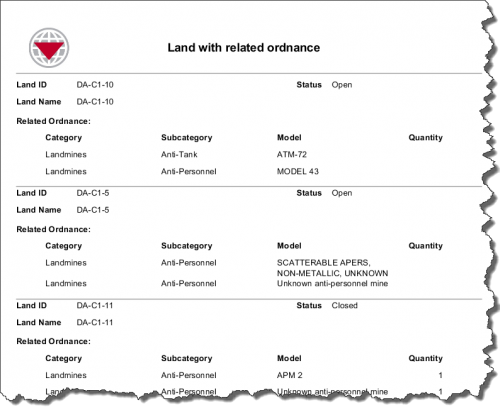
Because iReport templates are initiated with a search, they provide a scalable reporting solution that allows one template to be developed for many reports. For example, a report template that shows a list of land with associated ordnance details can produce different reports depending on the search parameters.
Report Example Using No Search Parameters
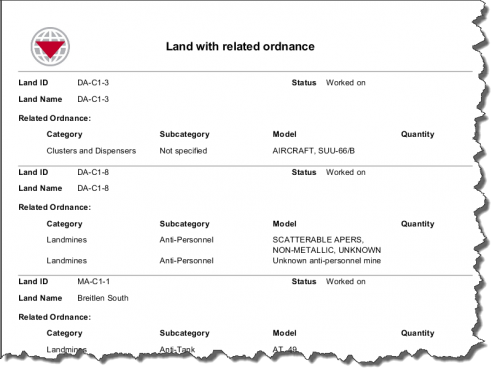
In the first example, no search parameter is applied and all data in IMSMANG is used in the report. But by adding a search parameter, for example, limiting this to land whose status is Worked on, a different report is generated.
Report Example Using a Search Parameter
Moreover, if the land is further limited to a specific type, another report is generated, using again the same template. This way, information managers can build templates and searches to fulfill multiple reporting needs.
Reports created with iReport can be printed directly within IMSMANG or saved to an intermediate format such as .RTF, .PDF or .XLS for electronic transmission or additional editing or inclusion in other reports. iReport supports the inclusion of charts, images and headers and footers, and it acts as a complete reporting package.
Data Export
| How To |
|---|
IMSMANG also provides data export functionality designed to allow users to export data to external tools such as Microsoft Excel for additional reporting and analysis. This lets users take advantage of functionality in these tools such as sums, counts, charts, pivot tables and other data manipulation functions to format and present data. Users access this functionality by performing a search in IMSMANG and then exporting the results to .CSV format. Users can choose which columns to export, and the data can be manipulated in any external tool that supports .CSV.
Because data export is initiated with a search, it provides a flexible approach for getting data to an external tool. However, once the data is used in a tool outside of IMSMANG, it is impossible to control how this data is manipulated which may limit the consistency of reports produced in this way.
External Reporting Tools
IMSMANG also allows information managers to connect advanced reporting tools such as Crystal Reports or ArcGIS Desktop directly to its relational database for highly advanced report generation. With this capability, information managers can use custom reporting solutions to connect with IMSMANG, allowing for complete control of IMSMANG outputs. Or, managers can modify existing reporting solutions to connect to IMSMANG, which leverages technology already implemented in the programme and limits the need for retraining.
| |
When using external reporting tools we recommend to connect to the Staging area instead of the IMSMANG database. It does require knowledge about the IMSMA data model. Contact contact your GICHD IM advisor if you have questions. |
Connecting other External Reporting Tools
The process for connecting external reporting tools is essentially the same for all tools. External tools connect to the IMSMANG relational database via an ODBC connection. Information managers establish this connection by installing the ODBC driver for PGSQL. When this is complete, information managers can connect any ODBC-compliant tool to the IMSMANG database, including reporting tools, other database packages and SQL management tools. Examples include:
| Reporting tools | Database packages | SQL management tools |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal Reports | Microsoft Access | PGSQL Query Browser |
| ArcGIS Desktop | OpenOffice Base | Navicat |
| iReport | Microsoft SQL Server | TOAD SQL |
| Microsoft Excel | Oracle | Heidi SQL |
When connecting an external reporting tool to IMSMANG, it is recommended that information managers build database views within the database to do any necessary data transformations. While it is possible to directly import or connect IMSMANG database tables in external tools and perform transformations within the external tools, the recommended method is to do transformations within the IMSMANG database using database views and then import the resulting views into the external tools.
| |
Building database views to transform data before importing it into other tools significantly reduces the performance hit associated with connecting external tools. |
Building Database Views
Building database views is the primary way of transforming data to support external reporting. Information managers can use SQL editing tools to build and save database queries as views that can be used to format data for easier reporting. Using database views, information managers can join data together into flat tables that allow for easier incorporation into reports or other analysis tools. Database views act like database tables and can be imported or queried from external tools. Moreover, views automatically refresh as data is added to IMSMANG and provide an up-to-date data source for other applications.
Using database views, information managers can perform statistical and other operations on the IMSMANG set for reporting purposes including sum, count and average or more complicated functions available in SQL. These operations can be combined with search criteria to provide a highly precise mechanism for providing data to reports. For example, information managers can create a view that returns the name of each clearance and a sum of the hours worked, AP mines found and area cleared on all progress reports linked to each clearance.
| Clearance ID | Area cleared | AP mines found | Hours worked | Number of progress reports |
| CL-1022 | 23,400 | 45 | 120 | 4 |
| CL-1239 | 22,330 | 42 | 160 | 6 |
| CL-2345 | 1,920 | 4 | 20 | 1 |
This view could then be pasted into Excel, linked with additional IMSMANG data or external data or linked with a map to provide additional analysis. As such, database views provide a powerful way of formatting and analysing IMSMANG data.
| |||||||||||||||||||