Creating Ad Hoc Views in MINT: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC right}} | {{TOC right}} | ||
== What is an ad hoc view? ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
The ad hoc editor allows the ''ad hoc'' exploration of data - typically the data from a [[Creating MINT Domains|Domain]]. It is meant for users who would like to explore data, as opposed to running a pre-defined report that allows for only little interactivity. | |||
== What is an | |||
The | |||
== Create an Ad Hoc View ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | == Create an Ad Hoc View ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| Line 10: | Line 8: | ||
<li>In the top-level menu, choose '''Create → Ad Hoc View''' | <li>In the top-level menu, choose '''Create → Ad Hoc View''' | ||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_create.png|center]]</li> | [[File:MINT_adhoc_create.png|center]]</li> | ||
<li>In the Data | <li>In the '''Select Data''' window, select the data the Ad Hoc View should be based on - this can be either a '''domain''' or a '''topic'''. In the Select Data window it is possible to switch between a list and a tree view by clicking on the respective icon in the top left corner. The list view provides a list of all available domains and topics in a flat structure (including those from the '''Public''' folder, if any), whereas the tree view presents them according to the repository folder structure. Select a domain or topic and click on '''Choose Data...'''. <br /> | ||
[[File: | List view: | ||
<li>In the next step, from all the attributes available from the chosen | [[File:MINT_adhoc_choose_data_list.png|center]]</li> <br /> | ||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_select_fields.png|center]]</li> | Tree view: | ||
<li> | [[File:MINT_adhoc_choose_data_tree.png|center]]</li> | ||
[[File: | <li>In the next step, from all the attributes available from the chosen domain/topic, select all those that should be included in the ad hoc view. Attributes can either be double-clicked or dragged and dropped to the right-hand pane named '''Selected Fields'''. Of course, if required, all available attributes can be selected. | ||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_select_fields.png|center|1200px]]</li> | |||
<li>Additional (optional) options can be specified at this stage: | |||
<ol> | |||
<li>'''Pre-Filters:''' the data for the ad hoc view can be filtered on any available attribute - for example, only accidents that happened in a specified date range could be considered</li> | |||
<li>'''Display:''' the order of appearance of the attributes can be changed, for example for ordering them logically</li> | |||
<li>'''Save as Topic:''' the specified selection of attributes, pre-filters and displays can be saved as another object type called '''Topic'''. A topic can also be the basis for an ad-hoc view.</li> | |||
</ol> | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_options.png|center]]</li> | |||
<li>Finally, click '''OK''' to validate the selection and proceed to the '''Ad Hoc Editor'''.</li> | |||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
== The Ad Hoc Editor ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_interface.png|center|900px]] | |||
=== Fields and Measures ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | === Fields and Measures ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Attributes available in the ad hoc interface (in the left-hand pane) are divided into two categories: '''fields''' and '''measures'''. Fields are non-numeric attributes, such as text and date, and measures are numeric attributes. The reason for the separation is that different operations/manipulations can be applied to these sets. In particular, custom fields can be created based on measures to which pre-defined functions are applied. | |||
==== Create a new calculated measure ====__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
To create a new calculated measure, click on the small icon/arrow in the heading of the measures pane and select '''Create Calculated Measure...'''. | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_calculated_measure.png|center]] | |||
In the Calculated Measure window, the desired calculated field can be created by either entering a formula manually into the '''Formula''' text box, or by double-clicking on available attributes and functions and clicking on the proposed mathematical and logical operators such as '''+''', '''AND''', etc. The following example shows the calculation of the percentage difference between the manually entered area size of a land and the area calculated based on the polygon defined for the same land. | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_new_calculated_measure.png|center]] | |||
The resulting calculated measure '''areasize_calcarea_diff_percentage''' is then available in the list of measures and can be used in the ad hoc view. It is also possible to create hierarchies of calculated measures, i.e. using calculated measure in the definition of another one. This thus allows to define new attributes on-the-fly, based on available ones. | |||
{{Note|These calculated measures are available only within the specific ad hoc view in which they are defined. If specific calculated measures should be available for all users and ad hoc views, then they should be created as calculated fields in the domain designer.}} | |||
=== The main ad hoc pane ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
In order to start an analysis, fields and measures can be dragged and dropped into the '''Columns''' and '''Rows''' boxes in the central ad hoc pane. Alternatively, it is possible to right-click on a field or measure and select either '''Add to Columns''' or '''Ad to Rows'''. The main ad hoc pane is automatically refreshed as attributes are defined as columns and rows. | |||
Data can be visualised in three different ways: in a table, a chart, or a crosstab. It is possible to switch between those views with the following drop-down in the main ad hoc pane: [[File:MINT_adhoc_type_switch.png]] | |||
=== Tables ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | === Tables ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Tables are used to display columns of data, with the possibility of grouping by attributes placed as rows. For example, in order to display several attributes of land grouped by provinces, an attribute ''Province'' would be placed in '''Rows''', and the other attributes in '''Columns'''. This will display one row per land recorded in the database. However, since there is a grouping by province, it might be interesting as well to display the totals by province. In order to change between displaying details, details and totals and totals only, click on the gear-wheel icon right above the data table: | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_table_details_totals.png|center]] | |||
=== Charts ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | === Charts ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Several different chart types are available in MINT to visually display data. Each chart type has its own display rules. If a chart requires a specific number of attributes in '''Columns''' and '''Rows''', then a brief help text is displayed. The best way to get familiar with different chart types is to try them out on real data. | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_chart_types.png|center]] | |||
=== Crosstabs ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | === Crosstabs ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
Crosstabs act like pivot tables, i.e. they allow displaying measures according to several combinations of dimensions, and summarising data for each dimension. The following example shows a crosstab displaying areasizes by province, status and contamination type, as well as totals by province, status and contamination type. | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_crosstab_example.png|center]] | |||
=== Filters ===__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
Finally, ad hoc views allow filtering on any of the available attributes. In order to filter the data on an attribute, drag and drop this attribute to the far right pane (if it is collapsed, it will expand as soon as an attribute is placed there). Depending on the type of the attribute (text, date, number), several filter types are available. For example, if the attribute '''Status''' (from the Land object) is used as a filter, and the attribute takes three different possible values in the database (Closed, Open and Worked on), then the following default filter is displayed: | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_filter_status.png|center]] | |||
Note that the filter type is set to '''equals'''. This can be changed by clicking on the arrow close to the filter type. The following options are available for a text attribute: | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_filter_options_text.png|center]] | |||
For a numeric attribute, the options are different: | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_filter_options_number.png|center]] | |||
{{Warning | When creating or changing a filter, make sure to always click '''Apply''' - only then the new filter criteria are taken into account.}} | |||
== Save an ad hoc view and create a report ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
The following options are available when saving an ad hoc view: | |||
* '''Save Ad Hoc View''': saves changes made to a an already existing ad hoc view. If a new ad hoc view is saved, this option has the same behavior as '''Save Ad hoc View As...'''. | |||
* '''Save Ad Hoc View As...''': saves a newly created ad hoc view (or allows to save an existing one with another name and/or in another folder). A repository folder needs to be selected as the location of the ad hoc view. | |||
* '''Save Ad Hoc View and Create Report''': this option allows saving the ad hoc view in a specific repository folder '''and''' the saving the analysis as a [[Creating Reports in MINT|report]] into the same or another folder. Different names need to be specified for the ad hoc view and the report, event if they are saved into two different folders. | |||
[[File:MINT_adhoc_save.png|center]] | |||
== | == Edit an ad hoc view ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
An ad hoc view can be edited/changed by clicking on its name in the repository, or by selecting the row and clicking on '''Open'''. This opens the ad hoc view in the editor and allows changing the ad hoc view. | |||
== Export data ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | == Export data ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
An ad hoc view in MINT can be used to export data from the database into a file. Any ad hoc view can be exported in the following formats: | |||
{{NavBox | [[File:MINT_adhoc_export_data.png|center]] | ||
[[Category: | MINT can thus be used as an easy to use shortcut for exporting data into an Excel file for example. When exporting data, the entire data from the ad hoc view gets exported, regardless if the option '''Sample Data''' or '''Full Data''' is chosen in the ad hoc view editor. | ||
{{NavBox Hub}} | |||
[[Category:NoPublic]] | |||
Latest revision as of 20:11, 20 February 2020
What is an ad hoc view?
The ad hoc editor allows the ad hoc exploration of data - typically the data from a Domain. It is meant for users who would like to explore data, as opposed to running a pre-defined report that allows for only little interactivity.
Create an Ad Hoc View
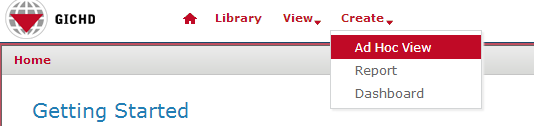
To create an ad hoc view:
- In the top-level menu, choose Create → Ad Hoc View
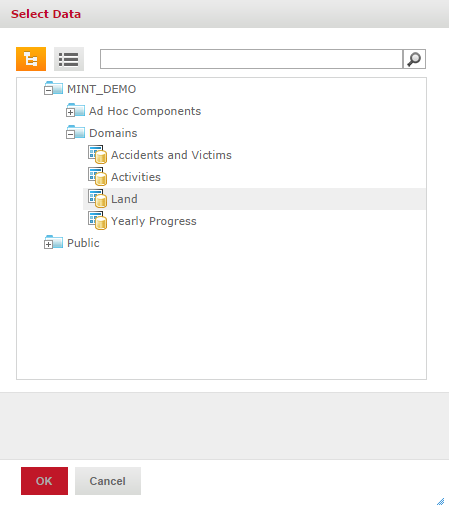
- In the Select Data window, select the data the Ad Hoc View should be based on - this can be either a domain or a topic. In the Select Data window it is possible to switch between a list and a tree view by clicking on the respective icon in the top left corner. The list view provides a list of all available domains and topics in a flat structure (including those from the Public folder, if any), whereas the tree view presents them according to the repository folder structure. Select a domain or topic and click on Choose Data....
List view: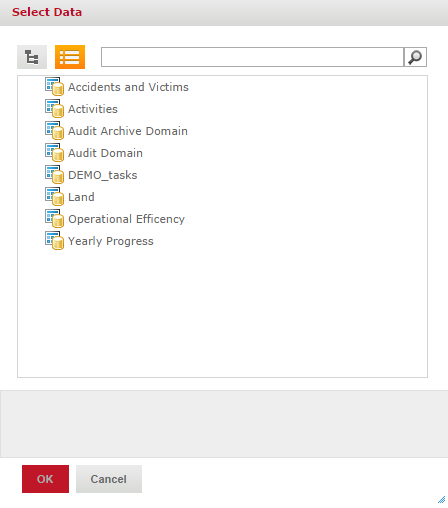
- In the next step, from all the attributes available from the chosen domain/topic, select all those that should be included in the ad hoc view. Attributes can either be double-clicked or dragged and dropped to the right-hand pane named Selected Fields. Of course, if required, all available attributes can be selected.
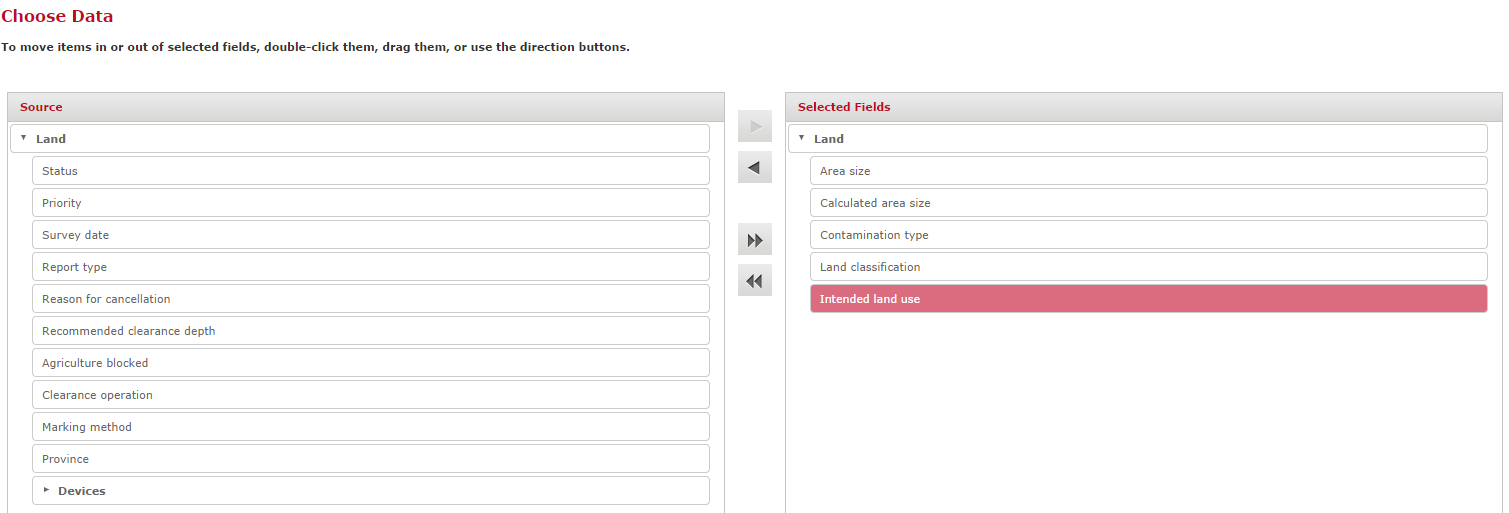
- Additional (optional) options can be specified at this stage:
- Pre-Filters: the data for the ad hoc view can be filtered on any available attribute - for example, only accidents that happened in a specified date range could be considered
- Display: the order of appearance of the attributes can be changed, for example for ordering them logically
- Save as Topic: the specified selection of attributes, pre-filters and displays can be saved as another object type called Topic. A topic can also be the basis for an ad-hoc view.

- Finally, click OK to validate the selection and proceed to the Ad Hoc Editor.
Tree view:
The Ad Hoc Editor
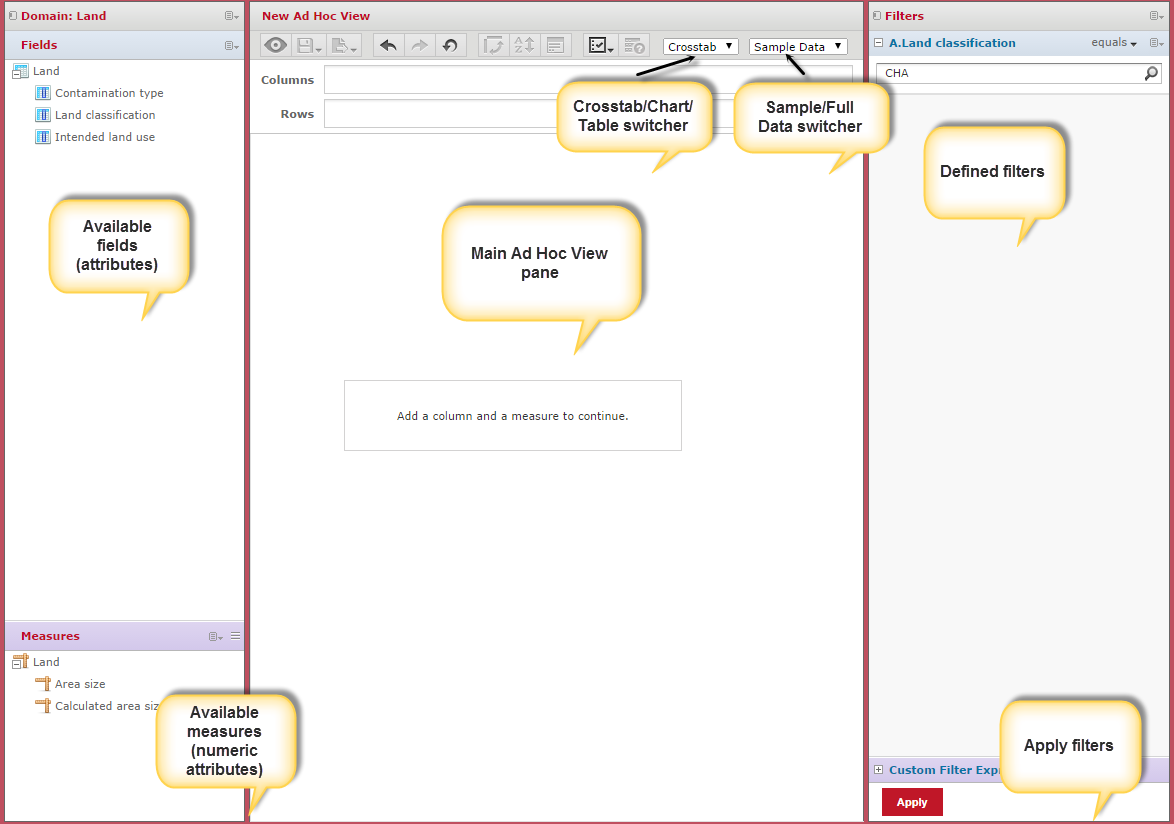
Fields and Measures
Attributes available in the ad hoc interface (in the left-hand pane) are divided into two categories: fields and measures. Fields are non-numeric attributes, such as text and date, and measures are numeric attributes. The reason for the separation is that different operations/manipulations can be applied to these sets. In particular, custom fields can be created based on measures to which pre-defined functions are applied.
Create a new calculated measure
To create a new calculated measure, click on the small icon/arrow in the heading of the measures pane and select Create Calculated Measure....
In the Calculated Measure window, the desired calculated field can be created by either entering a formula manually into the Formula text box, or by double-clicking on available attributes and functions and clicking on the proposed mathematical and logical operators such as +, AND, etc. The following example shows the calculation of the percentage difference between the manually entered area size of a land and the area calculated based on the polygon defined for the same land.
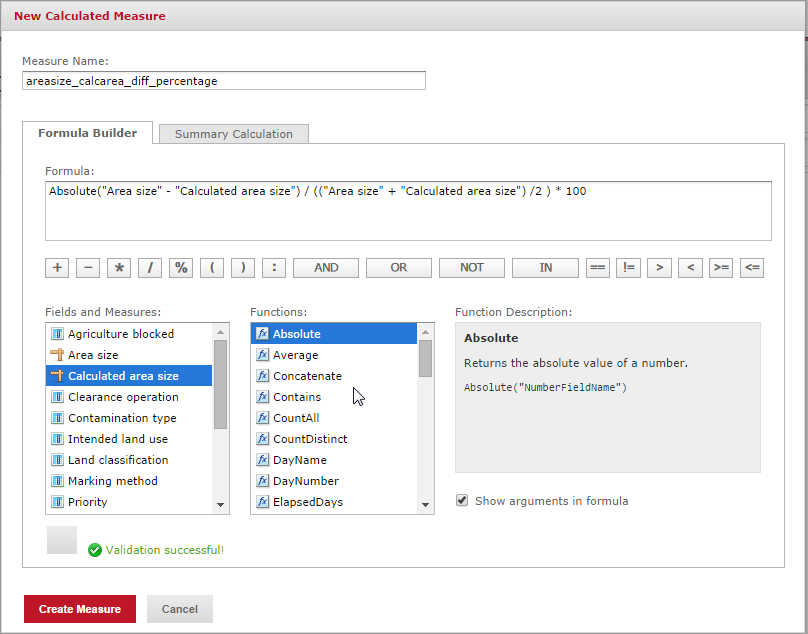
The resulting calculated measure areasize_calcarea_diff_percentage is then available in the list of measures and can be used in the ad hoc view. It is also possible to create hierarchies of calculated measures, i.e. using calculated measure in the definition of another one. This thus allows to define new attributes on-the-fly, based on available ones.
The main ad hoc pane
In order to start an analysis, fields and measures can be dragged and dropped into the Columns and Rows boxes in the central ad hoc pane. Alternatively, it is possible to right-click on a field or measure and select either Add to Columns or Ad to Rows. The main ad hoc pane is automatically refreshed as attributes are defined as columns and rows.
Data can be visualised in three different ways: in a table, a chart, or a crosstab. It is possible to switch between those views with the following drop-down in the main ad hoc pane: 
Tables
Tables are used to display columns of data, with the possibility of grouping by attributes placed as rows. For example, in order to display several attributes of land grouped by provinces, an attribute Province would be placed in Rows, and the other attributes in Columns. This will display one row per land recorded in the database. However, since there is a grouping by province, it might be interesting as well to display the totals by province. In order to change between displaying details, details and totals and totals only, click on the gear-wheel icon right above the data table:
Charts
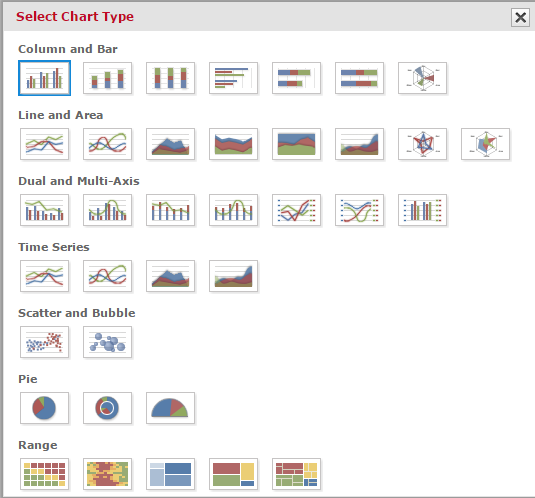
Several different chart types are available in MINT to visually display data. Each chart type has its own display rules. If a chart requires a specific number of attributes in Columns and Rows, then a brief help text is displayed. The best way to get familiar with different chart types is to try them out on real data.
Crosstabs
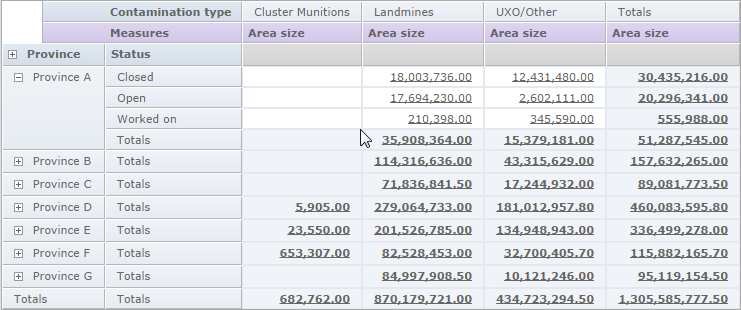
Crosstabs act like pivot tables, i.e. they allow displaying measures according to several combinations of dimensions, and summarising data for each dimension. The following example shows a crosstab displaying areasizes by province, status and contamination type, as well as totals by province, status and contamination type.
Filters
Finally, ad hoc views allow filtering on any of the available attributes. In order to filter the data on an attribute, drag and drop this attribute to the far right pane (if it is collapsed, it will expand as soon as an attribute is placed there). Depending on the type of the attribute (text, date, number), several filter types are available. For example, if the attribute Status (from the Land object) is used as a filter, and the attribute takes three different possible values in the database (Closed, Open and Worked on), then the following default filter is displayed:
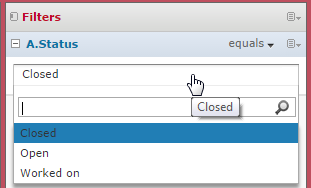
Note that the filter type is set to equals. This can be changed by clicking on the arrow close to the filter type. The following options are available for a text attribute:

For a numeric attribute, the options are different:

| When creating or changing a filter, make sure to always click Apply - only then the new filter criteria are taken into account. |
Save an ad hoc view and create a report
The following options are available when saving an ad hoc view:
- Save Ad Hoc View: saves changes made to a an already existing ad hoc view. If a new ad hoc view is saved, this option has the same behavior as Save Ad hoc View As....
- Save Ad Hoc View As...: saves a newly created ad hoc view (or allows to save an existing one with another name and/or in another folder). A repository folder needs to be selected as the location of the ad hoc view.
- Save Ad Hoc View and Create Report: this option allows saving the ad hoc view in a specific repository folder and the saving the analysis as a report into the same or another folder. Different names need to be specified for the ad hoc view and the report, event if they are saved into two different folders.
Edit an ad hoc view
An ad hoc view can be edited/changed by clicking on its name in the repository, or by selecting the row and clicking on Open. This opens the ad hoc view in the editor and allows changing the ad hoc view.
Export data
An ad hoc view in MINT can be used to export data from the database into a file. Any ad hoc view can be exported in the following formats:
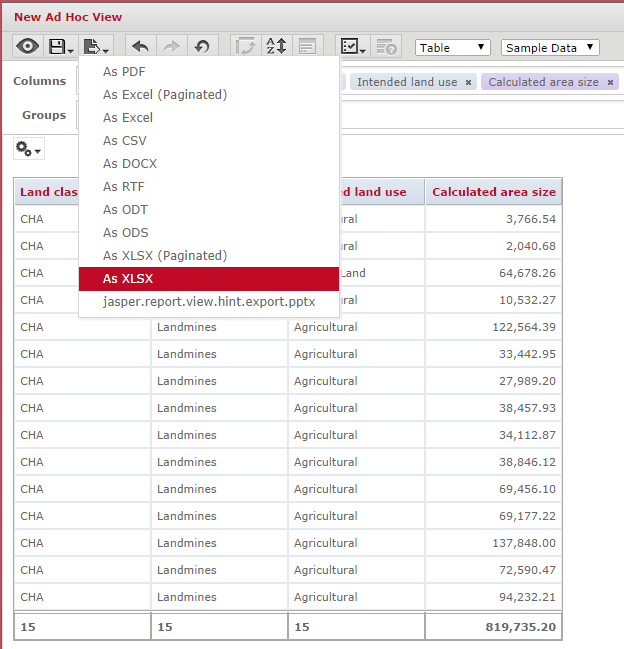
MINT can thus be used as an easy to use shortcut for exporting data into an Excel file for example. When exporting data, the entire data from the ad hoc view gets exported, regardless if the option Sample Data or Full Data is chosen in the ad hoc view editor. Template:NavBox Hub