| This page is under review |
After standardising auxiliary data, the next step in setting up IMSMANG is to implement the necessary customisation of the database reflecting the identified data requirements. Information managers have the possibility to modify the database in two ways:
- modifying existing data fields i.e. data fields that exist in the database from installation which often are referred to as system fields
- creating new data fields which are referred to as Custom Defined Fields (CDFs).
The objective of this step is to ensure that all data fields and values necessary for Mine action programme operation are available in IMSMANG. This step should be completed prior to designing Data Entry Form templates so that these changes are reflected on the Data Entry Forms.
| |
IMSMANG does not automatically change Data Entry Form templates when changes are made in the Data Inventory Manager. |
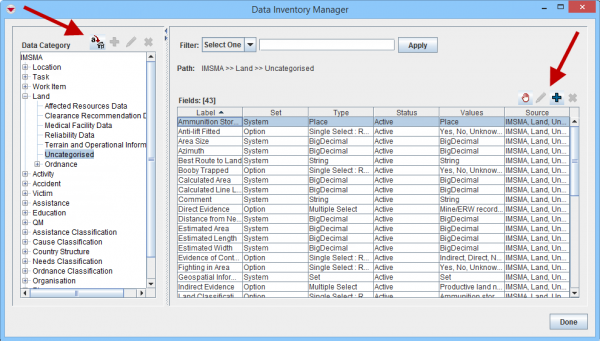
IMSMANG comes with more than 1,000 system fields from installation and therefore it is important to search in the Data Inventory Manager before adding CDFs in order to determine if a data field already exists before adding it as a CDF.
The Data Inventory Manager shows the data field by item and sub-categories so information managers can quickly navigate and find the data fields. It is also possible to add more categories and move fields between categories.
Data Inventory Manager Window
| |
If there are many fields/CDFs in one category the Data Inventory Manager may be slow to load. If that is the case then move fields/CDFs into a new or existing category. |
Contents
Modify Existing Fields
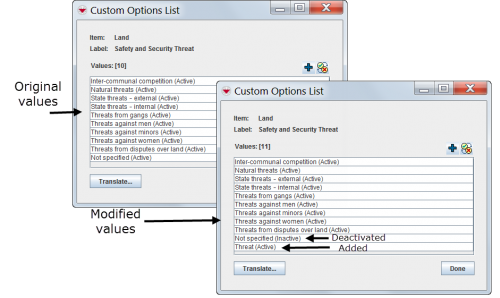
Using the Data Inventory Manager, information managers can customise the values of existing enumeration lists to reflect local programme needs. Information managers can add new values to the enumeration lists and deactivate existing values.
Modifying Data Fields
For example, the existing “Safety and Security Threat” data field for Land includes the values that are listed on the left side of the image. However, information managers can deactivate the values that their Mine action programmes don’t use and add the values that they do, as shown on the right side of the image.
While adding and deactivating new values is an effective and important capability within IMSMANG, information managers should approach changing the text of existing values carefully. Because many values are used across different data fields, for example, the values “Yes” and “No,” modifying these values can have unintended consequences.
Create New Data Fields
Information managers can create CDFs for those data fields not predefined in IMSMANG. IMSMANG does not limit the number of CDFs that can be created for each item; however, it is recommended that information managers use CDFs sensibly because the creation of many CDFs is a substantial contributor to poor system performance.
| How To |
|---|
When determining new data fields to add to IMSMANG, it is important to carefully consider the types of data to be collected and the format of the data. Using the correct data type for each field is critical to preserving the ability to search, calculate, sort and report information easily.
Dates, Text and Numbers
To create date, text and number fields in IMSMANG, information managers first select the type of item to create a CDF for and the type of CDF. Different types of fields make different operations available. For example, number fields enable calculations, date fields enable date searching and text fields enable text searching. After selecting the CDF, information managers provide a label and an optional description for the CDF.
| |
Text fields are limited to a set number of characters. Larger amounts of data can be attached to a Data Entry Form and stored in the database. |
IMSMA Enums (Multiple Select and Single Select)
Creating enumeration lists is one of the most powerful functionalities available in the IMSMANG Data Inventory Manager. Using this functionality, information managers can create rich data fields for each IMSMANG item that are searchable, translatable and customisable. Enumeration lists preserve data integrity by preventing problems associated with typographical errors, misspellings and other data entry errors, enabling users to compile and compare data easily. When created, the values for the enumeration lists can be modified to reflect changing needs over time.
Enumeration list data can be used in tools such as the Impact Scoring tool as well as in sorting and filtering. Data in single-select enumeration lists can be used to change the display of data on the map based on their values. For example, information managers can show different symbols on the map for different fields such as status, priority and type.
Creating a new enumeration list in IMSMANG requires information managers to first determine whether the enumeration list should allow the selection of single values (using radio buttons) or multiple values (using checkboxes). When this determination is made, the values for the enumeration list can be added and the enumeration list created. Information managers can also provide translations for the values, which automatically display for users running IMSMANG in other languages.
When the desired data fields are added to the Data Inventory Manager, information managers can proceed to form design to add the field to the data collection forms.
Using IMSMANG in a different language than English
IMSMANG provides the capability to translate and run the entire system in different languages. To fully translate the system into one or more languages, there are two parts to consider. The GUI i.e. what the user see and the data. How to translate the GUI is described here and how to translate the enumeration values and/or CDFs is described here. If the Mine Action programme needs to be multi-language e.g. Lao and English then two different sets of Data Entry Forms may be developed or the Data Entry Form may contain labels in both languages.
| |||||||||||||||||||