Difference between revisions of "Understanding Configuration Options"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
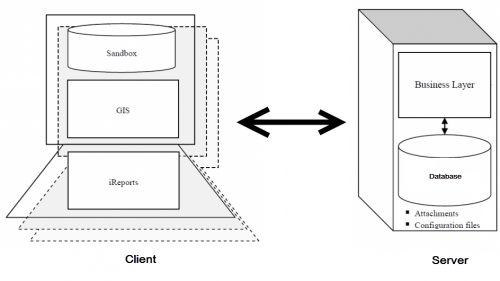
| + | ==Client-Server Architecture== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Whether a programme uses a stand-alone installation or a networked installation, the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> software has two main components: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> server | ||
| + | * the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> client | ||
| + | |||
| + | The figure below shows the parts of the software; the following sections then explain the functions that each part performs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Understanding Configuration Options- Client Server Architecture.png|center|500px|''Client Server Architecture'']] | ||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | ''Client-Server Architecture'' | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Server=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> server stores data and manages much of the data processing. The server has two main parts, the datastore and the business layer. The datastore is where data is stored for retrieval by the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> client. IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> uses a MySQL relational database to store data on the server. Additionally, IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> stores other data including attachments and some configuration files on the server in file format. The MySQL database is accessible via a variety of database access tools designed for browsing relational databases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The business layer is where rules are implemented to ensure data quality and consistency. The business layer takes data from the datastore and transforms it for display in the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> client. All data interaction between the client and server database is handled through the business layer, which allows for multiple clients to be connected to the database while preserving data integrity in cases of multiple requests. This includes access from the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> client and from the reporting tool. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Client=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> client is the interface through which users can connect to the server and browse the system, enter data and generate outputs. The client includes an integrated GIS and reporting tools. Based on ESRI’s ArcGIS Engine, the GIS performs all geospatial calculations including distance/bearing calculation, coordinate conversion and reprojection. The GIS also allows each client to load and manage its own maps and geographic data which the client receives from the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> server. As a result, each client receives and locally stores a complete copy of geographic data from the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> server when it is connected to the server. This synchronized data is stored in a client ―sandbox‖ separate from the server and can always be updated by connecting to the server. | ||
| + | |||
| + | JasperSoft’s iReport tool is built into each IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> client and allows users to access data from the database via the business layer. With iReport, users can generate reports containing tabular data, subreports and cross tabs as well as various types of charts and graphs. These reports can easily be localized into any language that IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> supports. Additional reporting options include direct connections to the IMSMA<sup>NG</sup> database via ODBC. This functionality supports tools such as Crystal Reports, Microsoft® Access®, Microsoft Excel® and various open-source reporting tools. | ||
Revision as of 08:22, 9 August 2012
To determine the initial configuration of the IMSMANG system, it is important to understand the two ways in which IMSMANG can be set up and the basic architecture of the system. IMSMANG is a client-server software application designed to run in stand-alone or networked mode.
| Configuration | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Standalone |
|
|
| Networked |
|
|
Client-Server Architecture
Whether a programme uses a stand-alone installation or a networked installation, the IMSMANG software has two main components:
- the IMSMANG server
- the IMSMANG client
The figure below shows the parts of the software; the following sections then explain the functions that each part performs.
Client-Server Architecture
Server
The IMSMANG server stores data and manages much of the data processing. The server has two main parts, the datastore and the business layer. The datastore is where data is stored for retrieval by the IMSMANG client. IMSMANG uses a MySQL relational database to store data on the server. Additionally, IMSMANG stores other data including attachments and some configuration files on the server in file format. The MySQL database is accessible via a variety of database access tools designed for browsing relational databases.
The business layer is where rules are implemented to ensure data quality and consistency. The business layer takes data from the datastore and transforms it for display in the IMSMANG client. All data interaction between the client and server database is handled through the business layer, which allows for multiple clients to be connected to the database while preserving data integrity in cases of multiple requests. This includes access from the IMSMANG client and from the reporting tool.
Client
The IMSMANG client is the interface through which users can connect to the server and browse the system, enter data and generate outputs. The client includes an integrated GIS and reporting tools. Based on ESRI’s ArcGIS Engine, the GIS performs all geospatial calculations including distance/bearing calculation, coordinate conversion and reprojection. The GIS also allows each client to load and manage its own maps and geographic data which the client receives from the IMSMANG server. As a result, each client receives and locally stores a complete copy of geographic data from the IMSMANG server when it is connected to the server. This synchronized data is stored in a client ―sandbox‖ separate from the server and can always be updated by connecting to the server.
JasperSoft’s iReport tool is built into each IMSMANG client and allows users to access data from the database via the business layer. With iReport, users can generate reports containing tabular data, subreports and cross tabs as well as various types of charts and graphs. These reports can easily be localized into any language that IMSMANG supports. Additional reporting options include direct connections to the IMSMANG database via ODBC. This functionality supports tools such as Crystal Reports, Microsoft® Access®, Microsoft Excel® and various open-source reporting tools.