PgSQL Replication: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This page describes how to set up direct replication with pgSQL. Generally, replication allows having two database servers (typically one for data entry and one for reporting) that stay synchronised. Concretely, when data is added, deleted or updated on the '''master''' server, the changes get immediately replicated on the '''slave''' or '''standby''' server. The standby database is read-only, i.e. no changes can be made directly there - only changes on the master are being replicated. Currently (August 2014) this mechanism is only in place at MACCA in Kabul. | This page describes how to set up direct replication with pgSQL. Generally, replication allows having two database servers (typically one for data entry and one for reporting) that stay synchronised. Concretely, when data is added, deleted or updated on the '''master''' server, the changes get immediately replicated on the '''slave''' or '''standby''' server. The standby database is read-only, i.e. no changes can be made directly there - only changes on the master are being replicated. Currently (August 2014) this mechanism is only in place at MACCA in Kabul. | ||
== Requirements ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
* Two computers/servers that can communicate with each other over the network. The communication goes over the port number 5432 (in a default setup), thus there might be firewall settings to be adapted, to ensure that the 5432 port on each computer is accessible for the other one. | |||
* The '''exact same''' IMSMA version on both computers. | |||
== Steps for stetting up the replication with pgSQL ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | == Steps for stetting up the replication with pgSQL ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
'''On the master server, with IMSMA database already installed:''' | |||
<ol> | |||
<li>Create a new user on the database by running the following SQL on the IMSMA database: | |||
<pre>CREATE USER replicator REPLICATION LOGIN ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'password';</pre> | |||
</li> | |||
<li>Uncomment and edit the following lines in the '''postgresql.conf''' file in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data: | |||
<pre> | |||
row 153 wal_level = hot_standby | |||
row 174 checkpoint_segments = 8 | |||
row 196 max_wal_senders = 3 | |||
row 199 wal_keep_segments = 8 | |||
</pre> | |||
The numbers on the left correspond to the number of the line. | |||
</li> | |||
<li>Add the following line in the '''pg_hba.conf''' file in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data: | |||
<pre> | |||
host replication replicator <standby-ip>/32 trust | |||
</pre> | |||
<standy-ip> is the IP address of the standby server (to be determined by running the command <pre>ipconfig /all</pre> in a command window) | |||
</li> | |||
<li> | |||
Restart the PGSQL service | |||
</li> | |||
</ol> | |||
'''On the standby server, also with IMSMA installed:''' | |||
<ol> | |||
<li>Stop the PGSQL service and delete all the contents of C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data</li> | |||
<li>Open a command window, cd into the directory C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/bin and run the following command: | |||
<pre> | |||
pg_basebackup –h <master-ip> -D c:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data –U replicator –v –P | |||
</pre> | |||
This command makes the initial synchronisation, i.e. copies the entire database from the master to the standby. This can take some time, depending on the size of the database. The progress can be followed on the command window as shown below.<br /> | |||
[[File:Pgsql replication basebackup1.png]]<br /> | |||
The following warning message can be ignored:<br /> | |||
[[File:Pgsql replication basebackup2.png]]<br /> | |||
{{Note|The hot standby replication mechanism can only be applied to the '''entire''' database server, i.e. all the databases from the master will be replication to the standby -- not only the database ''imsma'' but any database that is running on the master.}} | |||
</li> | |||
<li> | |||
Create a new file called '''recovery.conf''' in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data with the following contents: | |||
<pre> | |||
standby_mode = 'on' | |||
primary_conninfo = 'host=<master-ip> port=5432 user=replicator' | |||
</pre> | |||
<master-ip> is the IP address of the master server. | |||
</li> | |||
<li> | |||
Uncomment and edit the following lines in '''postgresql.conf''' in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data: | |||
<pre> | |||
210 hot_standby = on | |||
</pre> | |||
</li> | |||
<li>Restart the PGSQL service | |||
{{Note|Depending on the master and standby systems, there might need to be changes made to the '''pg_hba.conf''' file, such as commenting the lines relating to IPv6 local connections. Contact VIE if there are any troubles with this.}} | |||
</li> | |||
</ol> | |||
== Testing the replication ==__NOEDITSECTION__ | |||
After having set up the replication, it is good practice to perform a few tests. These can typically include the following: | |||
* Add/edit/delete data on the master server and verify that the changes are replicated to the standby. | |||
* Verify that he standby is read-only (this is very important for data consistency) by trying to edit something directly on the standby. There should be an error message such as "Error approving fieldreport" when trying to save/approve a new object or edit an existing object in IMSMA. | |||
* Shut down the standby, make changes on the master, start the standby and verify that all pending changes have been applied. | |||
{{NavBox Hub}} | {{NavBox Hub}} | ||
[[Category:NoPublic]] | [[Category:NoPublic]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:NAA]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:27, 20 February 2020
This page describes how to set up direct replication with pgSQL. Generally, replication allows having two database servers (typically one for data entry and one for reporting) that stay synchronised. Concretely, when data is added, deleted or updated on the master server, the changes get immediately replicated on the slave or standby server. The standby database is read-only, i.e. no changes can be made directly there - only changes on the master are being replicated. Currently (August 2014) this mechanism is only in place at MACCA in Kabul.
Requirements
- Two computers/servers that can communicate with each other over the network. The communication goes over the port number 5432 (in a default setup), thus there might be firewall settings to be adapted, to ensure that the 5432 port on each computer is accessible for the other one.
- The exact same IMSMA version on both computers.
Steps for stetting up the replication with pgSQL
On the master server, with IMSMA database already installed:
- Create a new user on the database by running the following SQL on the IMSMA database:
CREATE USER replicator REPLICATION LOGIN ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'password';
- Uncomment and edit the following lines in the postgresql.conf file in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data:
row 153 wal_level = hot_standby row 174 checkpoint_segments = 8 row 196 max_wal_senders = 3 row 199 wal_keep_segments = 8
The numbers on the left correspond to the number of the line.
- Add the following line in the pg_hba.conf file in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data:
host replication replicator <standby-ip>/32 trust
<standy-ip> is the IP address of the standby server (to be determined by running the commandipconfig /all
in a command window) - Restart the PGSQL service
On the standby server, also with IMSMA installed:
- Stop the PGSQL service and delete all the contents of C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data
- Open a command window, cd into the directory C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/bin and run the following command:
pg_basebackup –h <master-ip> -D c:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data –U replicator –v –P
This command makes the initial synchronisation, i.e. copies the entire database from the master to the standby. This can take some time, depending on the size of the database. The progress can be followed on the command window as shown below.

The following warning message can be ignored:
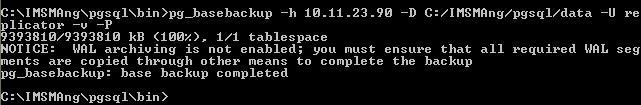
-
Create a new file called recovery.conf in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data with the following contents:
standby_mode = 'on' primary_conninfo = 'host=<master-ip> port=5432 user=replicator'
<master-ip> is the IP address of the master server.
-
Uncomment and edit the following lines in postgresql.conf in C:/IMSMAng/pgsql/data:
210 hot_standby = on
- Restart the PGSQL service
Testing the replication
After having set up the replication, it is good practice to perform a few tests. These can typically include the following:
- Add/edit/delete data on the master server and verify that the changes are replicated to the standby.
- Verify that he standby is read-only (this is very important for data consistency) by trying to edit something directly on the standby. There should be an error message such as "Error approving fieldreport" when trying to save/approve a new object or edit an existing object in IMSMA.
- Shut down the standby, make changes on the master, start the standby and verify that all pending changes have been applied.