Difference between revisions of "Managing Information Using IMSMANG"
Hradogoshi (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC right}} | {{TOC right}} | ||
| − | {{IMSMANG}} divides information management into three successive phases: recording, analysing and reporting. Each phase consists of different tasks that are performed using {{IMSMANG}} toolset. After an information manager decides how to customise {{IMSMANG}} for their organisation, the | + | {{IMSMANG}} divides information management into three successive phases: recording, analysing and reporting. Each phase consists of different tasks that are performed using {{IMSMANG}} toolset. After an information manager decides how to customise {{IMSMANG}} for their organisation, the IMSMA administrator sets up the toolset using the instructions in the wiki. The figure below shows the flow through the phases along with a brief description of the tasks performed in each. |
| − | + | {|align="center" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | |[[Image:IMPhaseIMSMA2.png|400px| ]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
==Recording==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Recording==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | In the | + | In the recording phase of information management, field officers enter a variety of details about an area, activity or event, otherwise known as an item, into {{IMSMANG}} using data entry forms. To ensure the right information is recorded, IMSMA administrators build and manage the data entry form templates and their item attributes, or portions of information to record for each type of item. {{IMSMANG}} provides a set of Inspiration templates with standard item attributes that IMSMA administrators can modify, or IMSMA administrators can build and publish custom templates with custom item attributes for the field officers to use. IMSMA administrators also set up and manage the country structure information and basic programme data, including ordnance, organisation and place data, that field officers use when completing data entry forms. |
==Analysing==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Analysing==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | An effective information management system enables an information manager to examine a large amount of data efficiently and make decisions that support their programme’s objectives. {{IMSMANG}} provides three customisable sets of tools for visualising and analysing mine action data and the tasks related to mine action activities. Themes enable users to display image-based information on the map, including icons to identify the location of an item by its type, high- resolution satellite images and topographic details. | + | An effective information management system enables an information manager to examine a large amount of data efficiently and to make that information available to those who make decisions that support their programme’s objectives. {{IMSMANG}} provides three customisable sets of tools for visualising and analysing mine action data and the tasks related to mine action activities. Themes enable users to display image-based information on the map, including icons to identify the location of an item by its type, high- resolution satellite images and topographic details. The summary view windows display a text-based summary of all the information entered into {{IMSMANG}} about an item. Working with their information managers, IMSMA administrators can customise these tools to display mine action data to suit the needs of the programme. IMSMA administrators can also design impact scoring templates, which enable the organisation to measure and report how much a location is affected by ordnance. |
==Reporting==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ==Reporting==__NOEDITSECTION__ | ||
| − | In the | + | In the reporting phase of information management, field officers compile mine action data and run a variety of reports for sharing information. Like {{IMSMANG}} other tools, the reports are customisable and stored as templates in the database so field officers can run the same reports as often as needed without configuring new reports each time. To support this work, IMSMA administrators create search definitions with most or all search criteria predefined and report templates for each item to report on depending on the attributes to be included, custom calculations that can be performed on the returned data if applicable and how the data should be formatted. |
| − | |||
{{NavBox Information Management}} | {{NavBox Information Management}} | ||
| + | [[Category:NAA]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:15, 27 May 2017
Contents |
IMSMANG divides information management into three successive phases: recording, analysing and reporting. Each phase consists of different tasks that are performed using IMSMANG toolset. After an information manager decides how to customise IMSMANG for their organisation, the IMSMA administrator sets up the toolset using the instructions in the wiki. The figure below shows the flow through the phases along with a brief description of the tasks performed in each.
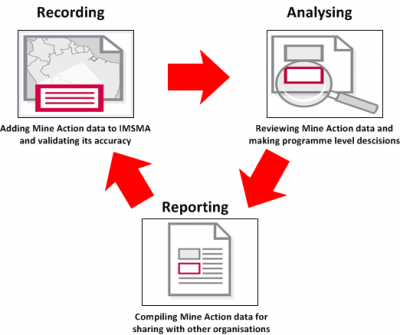
|
Recording
In the recording phase of information management, field officers enter a variety of details about an area, activity or event, otherwise known as an item, into IMSMANG using data entry forms. To ensure the right information is recorded, IMSMA administrators build and manage the data entry form templates and their item attributes, or portions of information to record for each type of item. IMSMANG provides a set of Inspiration templates with standard item attributes that IMSMA administrators can modify, or IMSMA administrators can build and publish custom templates with custom item attributes for the field officers to use. IMSMA administrators also set up and manage the country structure information and basic programme data, including ordnance, organisation and place data, that field officers use when completing data entry forms.
Analysing
An effective information management system enables an information manager to examine a large amount of data efficiently and to make that information available to those who make decisions that support their programme’s objectives. IMSMANG provides three customisable sets of tools for visualising and analysing mine action data and the tasks related to mine action activities. Themes enable users to display image-based information on the map, including icons to identify the location of an item by its type, high- resolution satellite images and topographic details. The summary view windows display a text-based summary of all the information entered into IMSMANG about an item. Working with their information managers, IMSMA administrators can customise these tools to display mine action data to suit the needs of the programme. IMSMA administrators can also design impact scoring templates, which enable the organisation to measure and report how much a location is affected by ordnance.
Reporting
In the reporting phase of information management, field officers compile mine action data and run a variety of reports for sharing information. Like IMSMANG other tools, the reports are customisable and stored as templates in the database so field officers can run the same reports as often as needed without configuring new reports each time. To support this work, IMSMA administrators create search definitions with most or all search criteria predefined and report templates for each item to report on depending on the attributes to be included, custom calculations that can be performed on the returned data if applicable and how the data should be formatted.